Has a doctor recently recommended Orchiopexy to you? This uncommon procedure may be recommended for infants, boys, or men, depending on the healthcare issue being treated. The procedure is effective and safe, but you may want to know more before considering it for an infant or yourself.
In this short guide, you’ll learn more about what this procedure is and when it is used. You’ll also get answers to other common questions.
What is an Orchiopexy?
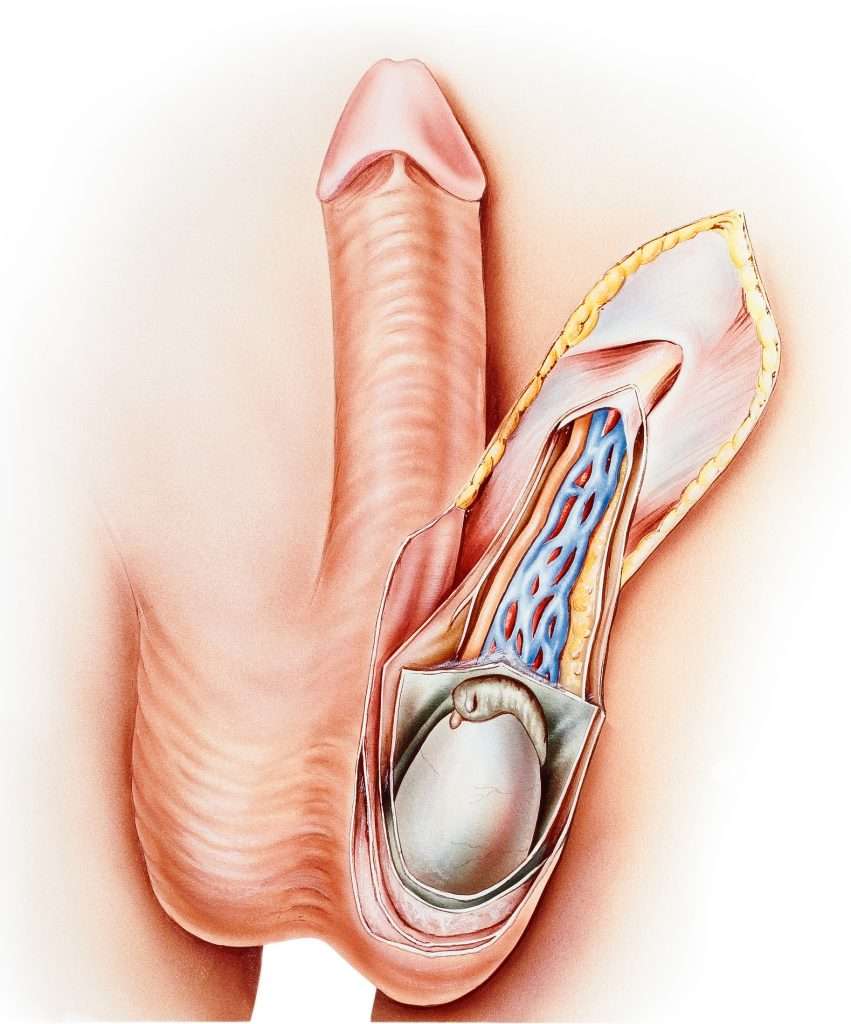
An orchiopexy is a surgical procedure that involves moving a testicle from the groin area to the scrotum. The operation prevents further injury to testicles, and reduces the risk of infertility and other serious complications that can rise from twisted or undescended testes.
In infants, this is often necessary when the testicles have failed to drop on their own. In young and adult males, it is usually necessary because an injury has occurred.
This procedure permanently resolves either issue. It binds the testicle to the scrotum, treating the problem and preventing it from happening again. Below, you can learn more about why this procedure may be necessary.
Why Orchiopexy is Needed: Undescended Testicles
Undescended testicles are a condition that may develop while the male fetus is still in utero. The testicles form inside the groin. When they finish this stage of development, they are supposed to drop into the scrotum either before birth or in the first few months of life.
When the testicles don’t drop properly, they are called “undescended.” About three in 100 babies will be born with undescended testicles. Premature babies are much more likely to experience this condition. As many as one in three babies will be affected.
The corrective pediatric procedure will often need to be performed in the first 12 to 24 months of age of the child’s life when it is judged that the infant is healthy enough for anesthesia, or when the treatment must be pursued to prevent injury.
The procedure involves small cuts to reach and then move the undescended testicle. As long as the testicle is healthy, it will be gently pulled out and allowed to fall into the right place. If the testicle is unhealthy, it may have to be replaced with a prosthesis.
Your child’s surgeon may also have to make other adjustments depending on other complications. Your doctor will discuss all the details with you before the time of the surgery.
Why Orchiopexy is Needed: Testicular Torsion
A testicular torsion is an injury where the cords that attach to the testes become twisted. This can happen due to the way the body develops, or in response to manipulation.
This procedure involves making a small incision and untangling the cords. Torsion can be dangerous because cutting off circulation to the testes can result in long-term damage. During the operation, your doctor will assess if the testicle can be saved or if it should be replaced with a prosthetic.
Common Questions About Orchiopexy
You may still have many more questions about how this procedure works and what to expect.
Is orchiopexy a major surgery?
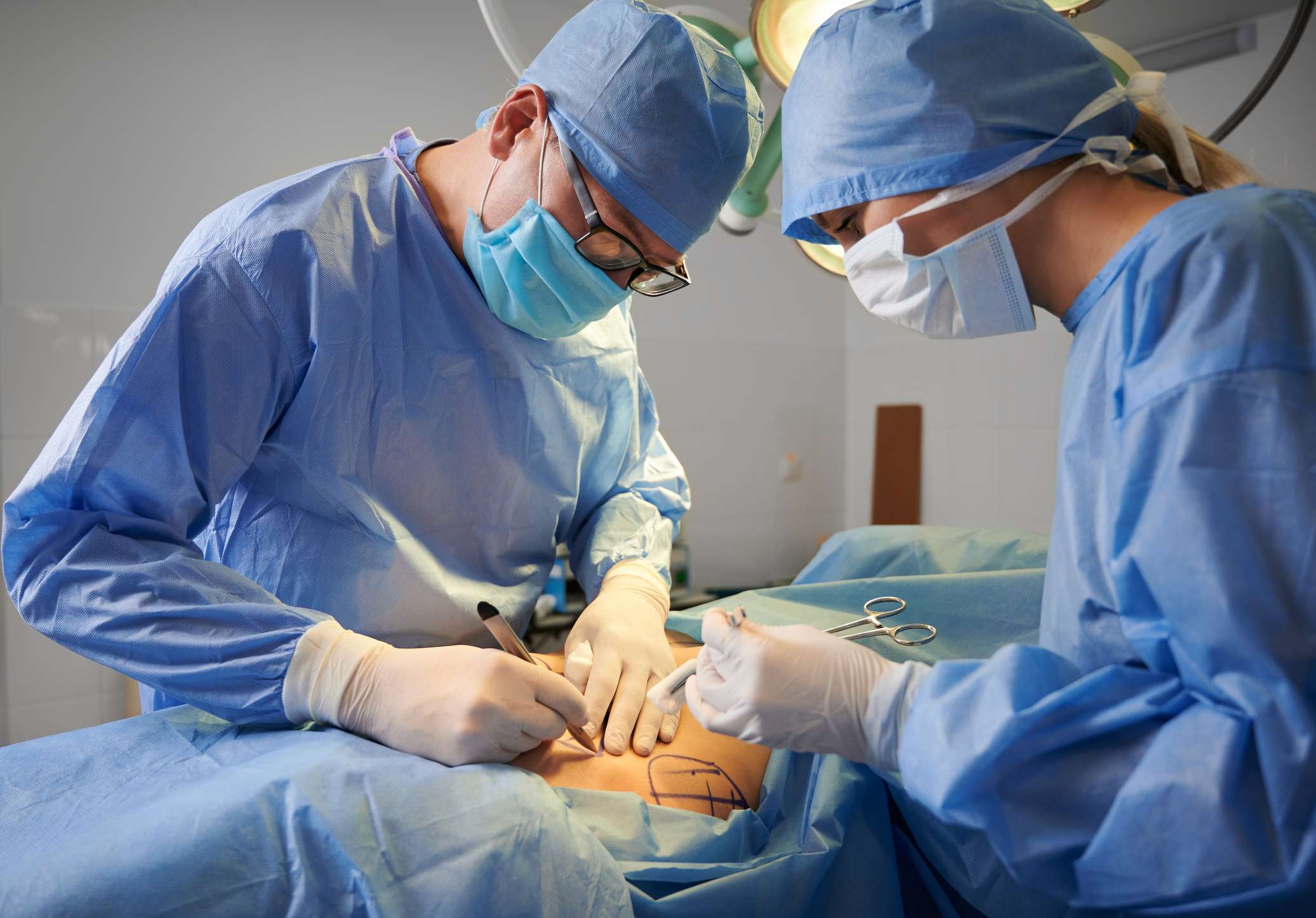
Orchiopexy is not considered to be a major surgery. This well-developed outpatient technique requires only tiny cuts to the scrotum skin. However, the removal of unhealthy testicles, or surgical stitching of the cords may require follow up surgeries that are more comprehensive than operations where the testicle is healthy and easily moved.
If the testicle is ready to be moved without complication, the resulting scar will often be small and can be made less visible by following the care steps provided by your doctor. Most patients will walk out after the surgery with mild recovery steps.
How painful is an orchiopexy?
Patients appear to report that this procedure is only minimally painful. Young children will be fully anesthetized, and adults will typically receive both general anesthesia and local anesthesia for pain management. It is rarely necessary to bear serious pain either during the operation or during the recovery period.
How long does an orchiopexy take?
This procedure most often takes no more than an hour. The time may be modified if your treatment requires some of the extra steps already discussed, such as the removal and replacement of unhealthy tests.
Only your doctor can provide you with a reliable timeline for the operation. It will be based on the unique factors of you or your child’s injury and health information. Your procedure may require adjustments or extra steps to ensure that you get the results you need.
Have More Questions? Contact Loria Medical
Now you understand Orchiopexy surgery and why it may be recommended for infants or older children, along with what conditions it can treat.
At Loria Medical, we focus on male enhancement, and scrotal surgeries are one of the many ways that we help our clients see what they expect from their bodies. Our clinic offers a complete range of scrotal enhancement treatments, including scrotal webbing correction.
In addition to scrotoplasty, we offer a range of other enhancement treatments for all parts of the penis. See our other treatment pages to learn more about how we can help you improve the look of the penile shaft, glans, and other areas.
To begin working with the Loria Medical team, contact us using our appointment form. Please leave a few details about your issue so we can determine whether we can help you with a consultation.